Introduction to Coconut Milk
Coconut milk nutrition facts – Coconut milk, a creamy and flavorful liquid extracted from mature coconuts, boasts a rich history intertwined with tropical cultures. Its origins trace back to the regions where coconut palms thrive, primarily in Southeast Asia, the Pacific Islands, and parts of the Americas. For centuries, it has served as a staple ingredient in countless culinary traditions, utilized in both sweet and savory dishes, beverages, and even beauty products.
Its versatility and nutritional profile contribute to its enduring popularity worldwide.Coconut milk’s production involves a relatively straightforward process. Mature coconuts are first husked and the hard outer shell is removed. The coconut water is often drained, though this depends on the intended use of the milk. The white flesh, or coconut meat, is then grated or shredded.
Understanding coconut milk nutrition facts is crucial for a balanced diet. Many recipes incorporate coconut milk alongside other ingredients, such as bread, and it’s helpful to consider the nutritional profiles of all components. For instance, a comprehensive understanding of the bread nutrition facts and ingredients can help you make informed choices when pairing it with coconut milk in dishes.
Ultimately, mindful consumption of both contributes to a well-rounded nutritional intake.
This shredded coconut meat is then mixed with warm water, allowing the coconut fat and other components to dissolve and create a milky emulsion. This mixture is then strained or squeezed to separate the creamy coconut milk from the fibrous coconut pulp. The resulting liquid is what we commonly know as coconut milk.
Types of Coconut Milk and Nutritional Variations
The type of coconut milk available significantly impacts its nutritional content. Full-fat coconut milk, extracted without removing any significant amount of fat, is rich in calories and saturated fat. However, it also provides a higher concentration of vitamins, minerals, and beneficial fatty acids like lauric acid. Light coconut milk, on the other hand, undergoes a process to reduce its fat content, resulting in fewer calories and less saturated fat.
This process often compromises the concentration of other nutrients as well. Additionally, some brands offer variations like “lite” or “low-fat” coconut milk, each with its own specific nutritional profile, typically reflecting different levels of fat removal. The labels usually clearly state the fat content and other nutritional information.
Coconut Milk Production Process, Coconut milk nutrition facts
The production of coconut milk begins with selecting mature coconuts, which are identified by their size, weight, and the sound they make when shaken (a mature coconut will have less liquid sloshing inside). After husking, the coconut is cracked open, and the coconut water is usually reserved for separate use. The white flesh is then carefully removed. Depending on the desired outcome (full-fat or light coconut milk), the extraction process varies.
For full-fat coconut milk, the entire coconut flesh is used. For light coconut milk, a portion of the fat is removed after the initial extraction. The shredded coconut flesh is then mixed with water and allowed to soak for a period before being strained or pressed to yield the desired coconut milk consistency. This process can be done manually or using industrial machinery, depending on the scale of production.
Nutritional Composition of Coconut Milk
Coconut milk, derived from the flesh of mature coconuts, offers a unique nutritional profile distinct from other plant-based milks. Understanding its macronutrient and micronutrient content is crucial for incorporating it effectively into a balanced diet. This section details the key nutritional components found in a typical serving of full-fat coconut milk.
Macronutrient Composition of Full-Fat Coconut Milk (per 100ml serving)
The following table presents the macronutrient breakdown of full-fat coconut milk, highlighting its significant fat content and moderate carbohydrate levels.
| Macronutrient | Amount | Unit | % Daily Value (approximate)* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fat | 27 | grams | ~41% |
| Carbohydrates | 4 | grams | ~1% |
| Protein | 1 | gram | ~2% |
*Percentage Daily Value is an approximation and can vary based on individual dietary needs and calorie intake.
Key Vitamins and Minerals in Coconut Milk (per 100ml serving)
Beyond macronutrients, coconut milk contributes several essential vitamins and minerals to the diet. While not as rich as some other plant-based sources, its contribution to overall nutrient intake should be considered.
| Nutrient | Amount | Unit | % Daily Value (approximate)* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Potassium | 170 | milligrams | ~4% |
| Magnesium | 15 | milligrams | ~4% |
| Vitamin C | 0 | milligrams | 0% |
*Percentage Daily Value is an approximation and can vary based on individual dietary needs and calorie intake. Note that Vitamin C content is negligible in coconut milk.
Types of Fats in Coconut Milk and Their Health Implications
Coconut milk is notably high in fat, primarily saturated fat. However, the type of saturated fat found in coconut milk differs from that in animal products. It contains a significant amount of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are metabolized differently than long-chain triglycerides (LCTs) found in most other fats.
While high saturated fat intake is generally linked to increased LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, studies on coconut milk’s impact are mixed. Some research suggests that MCTs may have less of a negative impact on cholesterol levels than LCTs and may even offer some metabolic benefits. However, it’s crucial to consume coconut milk in moderation as part of a balanced diet, considering individual health conditions and dietary goals.
Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term health effects of regular coconut milk consumption.
Coconut Milk and Dietary Considerations: Coconut Milk Nutrition Facts

Coconut milk’s versatility extends to its adaptability within various dietary approaches. Understanding its nutritional profile allows for its effective integration into diverse eating plans, while also acknowledging potential interactions with certain health conditions and medications.Coconut milk’s high fat content and relatively low carbohydrate count make it a popular choice in several dietary patterns. Its nutritional profile requires careful consideration, however, to ensure safe and effective incorporation into a balanced diet.
Coconut Milk in Different Diets
Coconut milk is naturally vegan, making it a suitable alternative to dairy milk in plant-based diets. Its creamy texture and rich flavor enhance vegan recipes, from curries to smoothies. For those following a ketogenic or low-carbohydrate diet, coconut milk can be a useful ingredient, providing healthy fats and contributing to satiety. However, it’s crucial to monitor portion sizes due to its calorie density.
For example, a ketogenic diet often emphasizes high-fat, moderate-protein, and very-low-carbohydrate intake; coconut milk, with its high fat content and relatively low carbohydrate content, can readily fit within these macronutrient ratios. However, individuals should be mindful of their overall daily carbohydrate intake and adjust their consumption accordingly.
Coconut Milk Interactions with Medications and Health Conditions
While generally safe for consumption, coconut milk may interact with certain medications or exacerbate specific health conditions. For individuals with thyroid issues, the high fat content of coconut milk could potentially interfere with thyroid medication absorption. Those with kidney disease might need to limit their intake due to the potassium content. Individuals on blood thinners should also exercise caution, as coconut milk may have blood-thinning properties that could interact negatively with prescribed anticoagulants.
It is always advisable to consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before significantly altering dietary intake, particularly when managing a pre-existing health condition or taking medication.
Incorporating Coconut Milk into a Balanced Diet
Coconut milk can be a delicious and nutritious addition to a balanced diet when consumed in moderation. It can be used as a base for soups and stews, added to smoothies for creaminess, or used in baking to replace some of the fat in recipes. A balanced approach involves incorporating coconut milk into a varied diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources.
For example, a balanced breakfast might include a smoothie with coconut milk, berries, and spinach, while a dinner could feature a curry made with coconut milk and plenty of vegetables. It’s essential to be mindful of portion sizes and to avoid over-consumption, particularly considering its calorie and saturated fat content. A balanced diet prioritizes variety and moderation; coconut milk should be incorporated as one element within a broader, healthy eating plan.
Visual Representation of Coconut Milk Nutrition
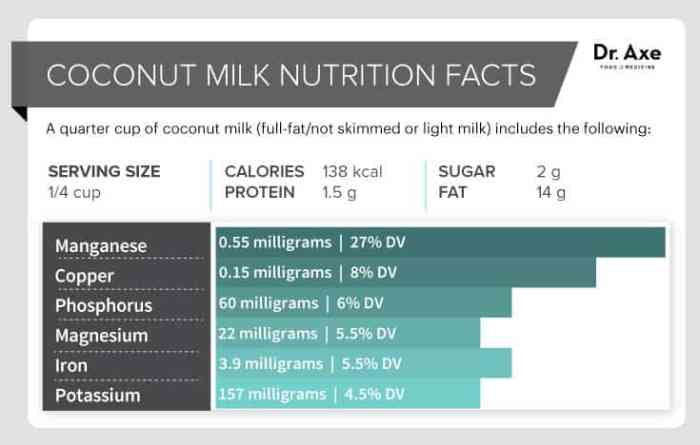
Understanding the nutritional profile of coconut milk is greatly enhanced by visual aids. These representations can effectively communicate the complex interplay of macronutrients and provide a quick, easily digestible overview of its composition. This section will explore both a visual depiction of the coconut itself and a graphical representation of its nutritional breakdown.
A mature coconut, roughly spherical and brown, possesses a hard outer husk (exocarp) which is usually removed before consumption. Beneath this lies the fibrous mesocarp (husk), which protects the hard shell (endocarp) containing the coconut water and the white coconut flesh (endosperm). The coconut milk is extracted primarily from the grated flesh, where the white endosperm is rich in fats and oils.
The process involves pressing or blending the flesh with water, resulting in a creamy white liquid with varying degrees of thickness depending on the amount of water added. The color of coconut milk ranges from a pale, almost off-white, to a creamy white, depending on the concentration and the variety of coconut used. The texture varies from a thin, watery consistency to a thick, almost viscous consistency, reflecting the fat content.
Coconut Macronutrient Composition Pie Chart
A pie chart effectively illustrates the proportion of macronutrients – carbohydrates, fats, and proteins – in a typical serving of coconut milk (approximately 1 cup or 240ml). Imagine a circle divided into three distinct segments, each representing a macronutrient. The largest segment, likely occupying over 50% of the circle, would represent fat, reflecting the high fat content of coconut milk.
This segment could be shaded a light cream or beige color to visually associate it with the color of coconut milk itself. A smaller segment, perhaps around 20%, would represent carbohydrates, possibly shaded a pale yellow or light brown. The smallest segment, representing protein, would occupy the remaining portion, perhaps only around 10%, and could be a light gray or pale green.
The remaining percentage would account for trace amounts of other nutrients and water. Each segment would be clearly labeled with the macronutrient name and its corresponding percentage, providing a clear and concise summary of the nutritional breakdown.
FAQ Explained
Is coconut milk suitable for people with lactose intolerance?
Yes, coconut milk is naturally lactose-free and a suitable alternative for those with lactose intolerance.
Does coconut milk contain cholesterol?
No, coconut milk does not contain cholesterol as it is a plant-based product.
Can coconut milk help with weight loss?
The high fat content of coconut milk can hinder weight loss if consumed excessively. Moderation is key.
How can I store coconut milk to maintain its freshness?
Store unopened cans of coconut milk in a cool, dry place. Once opened, refrigerate and use within a few days.
Is coconut milk good for athletes?
Coconut milk can provide electrolytes beneficial for athletes, but it should be part of a balanced sports nutrition plan.


